Ubuntu 19.04, aka “Disco Dingo“, is now available on all eRacks systems.
Canonical – The company behind Ubuntu published its regular (non-LTS) version as Ubuntu 19.04 (Disco Dingo) on April 18, 2019. The first Ubuntu 19.04 beta released on March 28. Other milestones during “Disco Dingo” development included feature freeze on February 21, 2019, UI freeze on March 14, 2019, and kernel freeze on April 1, 2019.
Up until this version, the codename of each Ubuntu release is traditionally made up of an adjective and an animal, both beginning with the same letter. But that’s only partly true this time – The word “Disco” is actually both a noun and a verb rather than adjective. A disco is a type of club or party at which people dance to music, often under lights.
A “Dingo” is a type of feral dog native to Australia and known for its sand-colored coat. Dingo dogs hunt alone or in cooperative packs. Inspired by the nature of the Dingo (which often sulks off when humans are around) the word has become informal Australian slang meaning ‘cowardly’, e.g., ‘he dingoes his way out of the date’.
Ubuntu 19.04 Disco Dingo is only the second Ubuntu release to use the letter ‘D’, following Ubuntu 6.06 “Dapper Drake” (released back in the land before time, aka 2006).
Since Ubuntu 19.04 (Disco Dingo) is a non-LTS version (not a Long Term Support version), it will be supported for 9 months until January 2020. If you need Long Term Support, it is recommended you use Ubuntu 18.04 LTS instead.
This article for Ubuntu 19.04 (Disco Dingo) provides an overview of the release and documents the known issues with Ubuntu 19.04 and its flavors.
Since the release of Ubuntu 19.04, everyone is talking about its Desktop Version. We’re going to do something a little different. We’re going to start with the Ubuntu 19.04 Server version first. Let’s what’s new:
Ubuntu 19.04 (Disco Dingo) Server Updates.
Every time Canonical releases a new version, it brings many new and noticeable changes. Each new version improves the previous one and strives to provide better user experiences.
Canonical made many changes on Ubuntu 19.04 (Disco Dingo) Server – the following are notable:
QEMU
In Ubuntu 19.04, QEMU was updated to the 3.1 release.
Migrations from former versions are supported just as usual. When upgrading it is always recommended to upgrade the machine types allowing guests to fully benefit from all the improvements and fixes of the most recent version.
Qemu now has virglrenderer enabled which allows to create a virtual 3D GPU inside qemu virtual machines. That is inferior to GPU pass-through, but can be handy if the platform used lacks the capability for classic PCI pass through as well as more modern mediated devices.
For more details, see the QEMU 3.1 change log.
LIBVIRT
Among many other changes worth to mention is the ability to have GL enabled graphics as well as mediated devices to be configured while still being guarded by custom apparmor profiles generated per guest. This is required for the use of GPU based mediated devices as well as VirGL (mentioned above in the QEMU section). For bringing these changes libvirt was updated to version 5.0.
DPDK
Ubuntu includes 18.11.x the latest stable release branch of DPDK. The very latest (non-stable) version being 19.02 was not chosen for downstream projects of DPDK (like Open vSwitch) not being compatible.
DPDK dependencies were reorganized into more or less common/tested components. Due to that most DPDK installations will now have a smaller installation footprint and less potentially active code to care about.
For more details see the release notes.
SAMBA
Samba was updated to version 4.10.x, and one of the big changes here is python3 support. In Disco, samba and its dependencies are all python3 only now, with the exception of tdb. tdb still builds a python2 package, namely python-tdb, but all the others, including samba itself, are python3 only.
Open-VM-Tools
To run well integrated as VMware guest Ubuntu 19.04 comes with the latest open-vm-tools version 10.3.10. Details about the changes can be found in the upstream changelog
Raspberry Pi
Ubuntu 19.04 comes with an easy way of enabling Bluetooth support on the raspi3 Ubuntu-server preinstalled images. Install the Pi-Bluetooth package (now available in multiverse) with ‘sudo apt install pi-bluetooth’.
Please note that supported Pi devices which have Bluetooth (at the time of writing, the Raspberry Pi 3B, 3B+, and 3A+) can have either serial console or Bluetooth support enabled at any given time (not both). With the Pi-Bluetooth package installed, edit it at ‘/boot/firmware/config.txt’ and set ‘enable_uart=1’ to enable serial console, or ‘enable_uart=0’ to enable Bluetooth. The change will take effect after the next reboot.
Open vSwitch
Open vSwitch has been updated to 2.11. This updated Open vSwitch version has support for the kernel versions 4.16.x and 4.17.x. Also the following features can be found on this version.
- “mod-table” command can now change OpenFlow table names.
- The environment variable OVS_SYSLOG_METHOD, if set, is now used as the default syslog method.
- The environment variable OVS_CTL_TIMEOUT, if set, is now used as the default timeout for control utilities.
- OVN-SB schema changed: duplicated IP with same Encapsulation type is not allowed any more. Please refer to Documentation/intro/install/ovn-upgrades.rst for the instructions in case there are problems encountered when upgrading from an earlier version.
- New support for IPSEC encrypted tunnels between hypervisors.
- ovn-ctl: allow passing user:group ids to the OVN daemons.
- IPAM/MACAM add the capability to dynamically assign just L2 addresses
- IPAM/MACAM add the capability to specify a static ip address and get the L2 one and it is allocated dynamically using the following syntax: ‘ovn-nbctl lsp-set-addresses <port> “dynamic <IP>”.’
Please read the Open vSwitch release notes for more detail.
OpenStack Stein
Ubuntu 19.04 includes the latest OpenStack release, Stein, including the following components:
- OpenStack Identity – Keystone.
- OpenStack Imaging – Glance.
- OpenStack Block Storage – Cinder.
- OpenStack Compute – Nova.
- OpenStack Networking – Neutron.
- OpenStack Telemetry – Ceilometer, Aodh, Gnocchi, and Panko.
- OpenStack Orchestration – Heat.
- OpenStack Dashboard – Horizon.
- OpenStack Object Storage – Swift.
- OpenStack Database as a Service – Trove.
- OpenStack DNS as a Service – Designate.
- OpenStack Bare-metal – Ironic.
- OpenStack Filesystem – Manila.
- OpenStack Key Manager – Barbican.
Please refer to the OpenStack Stein release notes for full details of this release of OpenStack.
WARNING: Upgrading an OpenStack deployment is a non-trivial process and care should be taken to plan and test upgrade procedures which will be specific to each OpenStack deployment. For Upgrading successfully please make sure you read the OpenStack Charm Release Notes for how to deploy Ubuntu OpenStack using Juju. Or simply contact eRacks Systems’ experts for help.
There are many other changes on newly released Ubuntu 19.04 non-LTS Server. Please read the Ubuntu 19.04 (Disco Dingo) non-LTS Server release note for more details.
Ubuntu 19.04 (Disco Dingo) Desktop (And Kernel) updates.
Linux Kernel 5.0.0-8 “Shy Crocodile”
The Linux Kernel had its number bumped to 5.0.0-8 by Linus Torvalds, but not because of particularly noteworthy code changes. Usually, a significant number jump like this would echo an equally significant code or functionality change, but that isn’t the case. In an email to the Linux Kernel Mailing List, he explained:
“The numbering change is not indicative of anything special. If you want to have an official reason, it’s that I ran out of fingers and toes to count on, so 4.21 became 5.0.”
Torvalds went on to give a breakdown of the code changes in Linux 5.0:
This new kernel should be faster, too, as work was done to speed up the anti-Spectre and Meltdown code.
GNOME desktop 3.32
Ubuntu 19.04 ships with the latest GNOME desktop 3.32. This brings performance improvements, a host of bug fixes and some important new features. Beyond the visual changes, GNOME itself is faster and uses fewer GPU resources thanks to work done by both Canonical and the upstream GNOME team.
Of course, there’s a new wallpaper in latest GNOME desktop 3.32. But the first thing you’ll probably notice is a new icon on the desktop for your home directory. If you don’t like it, you can install GNOME Tweaks and use it to hide the home directory icon.
In keeping with modern “flat” design, the desktop’s top bar and launcher have solid-black backgrounds. The application menus have been moved back to each application’s window. They no longer appear in the toolbar. That’s a change in GNOME and not a design decision from Canonical. Some applications always kept their menus in their own application windows, which made the experience inconsistent. There were also some long-standing issues that were tough to fix. Now, that whole initiative has been canned in favor of a traditional menu placement—each applications menu is in the application’s own window.
Fractional Display Scaling (Possibly)
GNOME 3.32 includes support for fractional scaling, which is of interest to people with high DPI (Dots Per Inch) displays.
Unfortunately, in the modified version of GNOME supplied with Ubuntu, the fractional scaling settings are either hidden or not accessible to us. Eventually, a tool might allow access to these settings—or another means of accessing those settings will emerge from the user community. After all, they’re in GNOME.
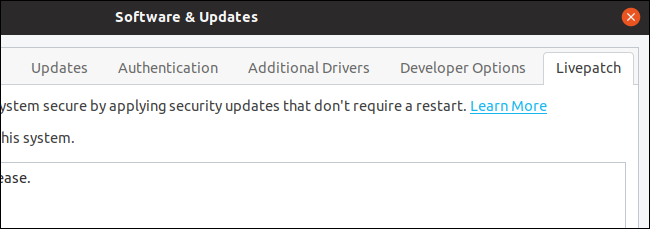
Live patch for Reboot-Free Kernel Updates
Canonical introduced Live patch in Ubuntu 18.04 LTS, only to remove it again in 18.10. It’s now back, complete with this new tab in Software & Updates.
Ubuntu 19.04’s Software and Updates app has a new tab called Live-patch. This new feature is intended to allow critical kernel patches to be applied without rebooting. For people using Ubuntu at home, on machines that get powered off frequently, requiring a power cycle to install a kernel update isn’t a hardship. If your Ubuntu computer is providing an external service or is hosting a website, it becomes trickier to try to schedule in the reboots.
New Icons and Visual Tweaks
The Yaru icon set has had a refresh, and new icons have been added to cater for more third-party applications. This icon set looks more coherent and slick. There’s evidence of attention being paid to the user interface all over. Files has had a facelift, and it looks crisp and feels responsive. That’s not a surprise.
Even the Terminal window has been polished up. The GNOME Terminal application has a new title bar with a prominent “New Tab” button and search icon.
The System menu has a new cogwheel Settings icon that replaces the old “crossed wrench and screwdriver” icon.
Application Permission Controls
GNOME’s Settings app now lets you control various application permissions. You can even choose whether or not each application can show notifications.
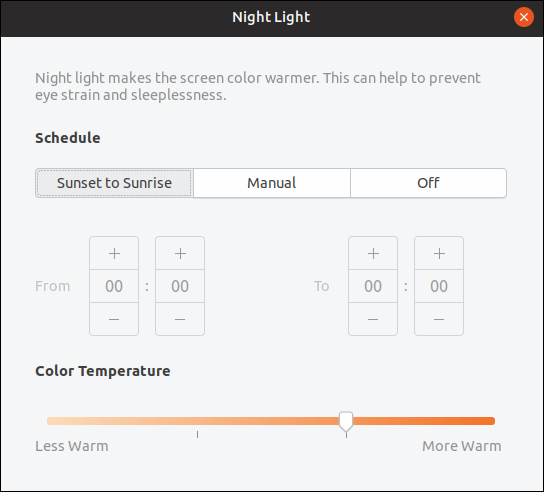
Night Light Improvements
The Night Light feature changes the hue of your computer’s display, reducing the amount of blue in the display illumination as the sun sets. You can now configure the schedule for the Night Light yourself. You can also select the color temperature—or “warmth”—of the display when Night Light is activated.
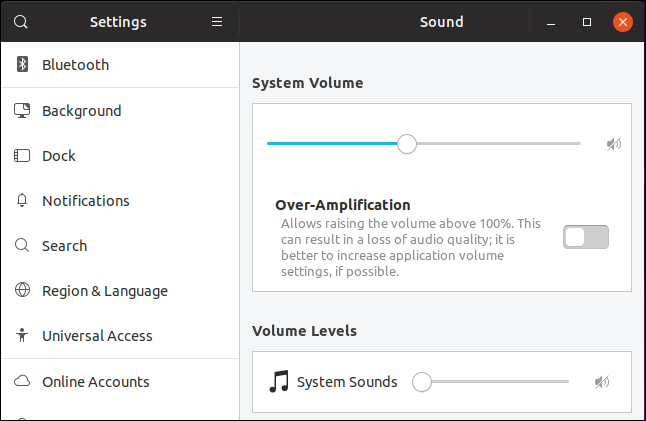
Updated Sound Controls
The Sound controls have been revamped. You don’t get more functionality than before, but the controls are laid out more conveniently and logically.
Raspberry Pi Touch Support
The bulk of the driver work in the kernel has been to graphics drivers, with enhanced support for displays ranging in size and capability—from the AMD FreeSync NVIDIA RTX Turing to the Raspberry Pi Touch Display. The Debian-derived Raspbian Linux already supported the Raspberry Pi Touch Display, but now you have the choice of using native Ubuntu with your Pi Touch.
There are many other changes as well. Some of them are mentioned below:
- Tracker is now included by default. This allows the desktop to keep track of recently used files and improves searching.
- Right click handling is now “area” by default. This allows both two-finger right clicking and clicking in the bottom right corner of the touchpad
- alt-tab handling now switches windows by default. Switching applications by default can be done with super-tab
- Preview order of windows in the dock is now static and based on the order in which the windows were added
- IWD can now be enabled for use with Network Manager. IWD is a new alternative to wpa supplicant and is in testing for consideration in the future.
- Installing Ubuntu Desktop on vmware will now automatically install the open-vm-tools package to improve integration.
- The Yaru theme has seen further refinement and updates and includes a new icon theme.
- Safe Graphics Mode. A new option is added to the Grub menu which will boot with “NOMODESET” on. This may help you resolve issues on certain graphics cards and allow you to boot and install any propriatary drivers needed by your system.
- The latest releases of Firefox (66.0) and LibreOffice (6.2.2) are available and installed by default.
Some of the Common New features and Updated Packages in both Ubuntu 19.04 (Disco Dingo) non-LTS Desktop and Server Version.
Linux kernel 🐧
Both Ubuntu 19.04 (Disco Dingo) non-LTS Desktop and Server are based on the Linux release series 5.0. It includes support for AMD Radeon RX Vega M graphics processor, complete support for the Raspberry Pi 3B and the 3B+, Qualcomm Snapdragon 845, many USB 3.2 and Type-C improvements, Intel Cannonlake graphics, significant power-savings improvements, P State driver support for Skylake X servers, POWER memory protection keys support, KVM support for AMD Secure Encrypted Virtualization, enablement of Shared Memory Communications remote and direct (SMC-R/D), Open for Business (OFB), and zcrypt on IBM Z among with many other improvements since the v4.15 kernel shipped in 18.04 LTS.
Toolchain Upgrades 🛠️
Ubuntu 19.04 comes with refreshed state-of-the-art toolchain including new upstream releases of glibc 2.29, ☕ OpenJDK 11, boost 1.67, rustc 1.31, and updated GCC 8.3, optional GCC 9, 🐍 Python 3.7.3 as default, 💎 ruby 2.5.5, php 7.2.15, 🐪 perl 5.28.1, golang 1.10.4. There are new improvements on the cross-compilers front as well with POWER and AArch64 toolchain enabled to cross-compile for ARM, S390X and RISCV64 targets.
There are many other changes on newly released Ubuntu 19.04 non-LTS verson. Please read the Ubuntu 19.04 (Disco Dingo) non-LTS release note for more or Disco Dingo Release Notes.
Get your system with Ubuntu 19.04 (Disco Dingo) as pre-installed from eRacks Systems’ show room with Quote request. Or download Ubuntu 19.04 (Disco Dingo) directly from below.